Ip message
Author: q | 2025-04-24
The advent of IP Messaging Service and evolution towards Converged IP Messaging. The Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) specified the SIMPLE IM technology as the first IP-based messaging

IP Message: Send Message to any IP Address - MUO
A DHCP client device acquires the IP address and the network parameters by broadcasting a UDP packet called DHCPDISCOVER within the network.Upon receiving the DHCPDISCOVER broadcast, all the non-authoritative servers discard or ignore the message. DHCP servers within the networks receive and process the broadcast packet.The DHCP Discover message contains details like: UDP Source Port 68 UDP Destination Port 67 Source IP 0.0.0.0 Destination IP 255.255.255.255 DHCPDISCOVER Packet contents Here, the source IP of the broadcast packet is 0.0.0, as the client device has not been assigned the IP address yet. With the destination IP as 255.255.255.255, the broadcast packet is sent to all the network devices, through a process called limited broadcast. Destination IP can be set to a particular subnet ID to enable a directed broadcast.Step 2: DHCP Server offers IP and network configuration parameters to client.When a valid DHCP server receives the DHCPDISCOVER broadcast message, it reserves an IP in its IP pool, and offers that IP on lease to the requesting client. It conveys its IP lease offer, the subnet mask, and default gateways to the requesting client through a DHCPOFFER message. UDP Source Port 68 UDP Destination Port 67 Source IP 192.168.31.9 Destination IP 255.255.255.255 DHCPDISCOVER Packet contents Here 192.168.31.9 is the DHCP server that offers an IP address from its pool. Traditionally, this offer message is sent to the client by specifying the clients hardware or MAC address.Step 3: Client acknowledges the required DHCP’s offer and requests the IP lease.Upon receiving a DHCPOFFER message, the client requests the assignment of the IP address offered through the DHCPOFFER message by sending a DHCPREQUEST message to the server. This message signals the DHCP server to allocate the offered IP address on lease to the client.On receiving more than one DHCPOFFER messages from the servers in the network, the client sends a DHCPREQ (DHCP Request) message only to the DHCP server whose message was received first by the client. Other offers are discarded or ignored. UDP Source Port 68 UDP Destination Port 67 Source IP 0.0.0.0 Destination IP 255.255.255.255 DHCPREQ Packet contents Step 4: DHCP Server acknowledges clients IP lease request.Upon receiving the DHCPREQUEST message, the DHCP server assigns the IP address to the client, and logs it in its data store. The server confirms the allocated IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway details by sending an DHCPACK (DHCP acknowledgement) message.The client can now start using the allocate IP and network parameters. UDP Source Port 68 UDP Destination Port 67 Source IP 192.168.31.9 Destination IP 255.255.255.255 DHCPACK Packet contents The DHCP client configures itself with the received network parameters.DHCP relay agentDevices can send broadcast messages only within the network they are a part of. They can
The Evolution of Messaging: How IP Messaging Is
Datagram. ICMP is a separate protocol from IP, but every IP implementation must include the ICMP protocol. ICMP makes use of the IP protocol as a transport and like IP, ICMP is best-effort; an ICMP message is not guaranteed to arrive at its destination.The purpose of ICMP is to provide feedback regarding the network and datagrams, it is not to make IP a reliable transport mechanism. ICMP messages use a basic IP datagram header with the IP data being the ICMP message. The IP source address is that of the host or gateway sending the ICMP message with the destination IP address being that of the original source IP address.RFC 792 states that, where applicable, each ICMP message contains the IP header and first 64 bits of the original datagram which is used to match the datagram to a process. RFC 1812 indicates that this is no longer adequate and an ICMP message, where applicable, should contain as much of the original datagram as possible that can fit within a 576 byte message.What is IP messaging. IP messaging has become new buzzword
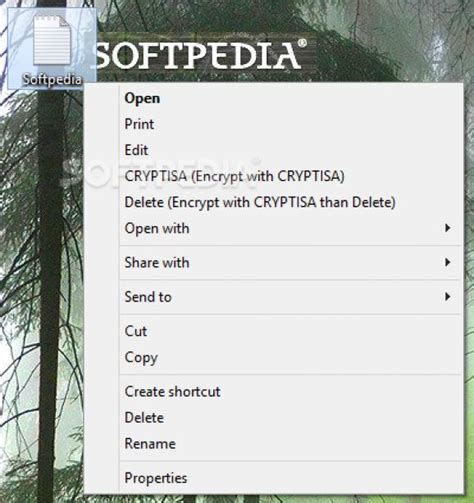
As from the menu. Encrypt and lock your messages with RSA and AES To encrypt and lock your messages with other users, you can use the encryption feature of IP Messenger. To do so, click on the lock icon in the send window or press Ctrl+Alt+L. You will see a lock window that asks you to enter a password or a fingerprint. You can also choose the encryption algorithm (RSA or AES) and the key length (128, 192, or 256 bits) from the drop-down menus. When you are done, click OK to lock your message. To receive encrypted and locked messages from other users, you will see a pop-up window that shows you their name, message, and lock icon. You can decrypt and unlock their message by clicking on the lock icon or pressing Ctrl+Alt+L. You will see a lock window that asks you to enter the same password or fingerprint that they used. If you enter the correct password or fingerprint, you will see their message and attachments or inline images. Conclusion IP Messenger is a secure and free LAN messaging software that you can use to communicate with your friends or colleagues on a local area network. It offers features such as file/folder transfer, inline image capture, message encryption, and powerful log viewer. It is also easy to download and install, and supports multiple platforms. If you are looking for a simple, lightweight, and secure way to communicate over LAN, you might want to give IP Messenger a try. FAQs Q: How can I change the language of IP Messenger?A: You can change the language of IP Messenger by clicking on the menu icon in the main window and selecting Language from the menu. You will see a list of available languages that you can choose from. Click on the language that you want to use and restart IP Messenger. Q: How can I change the settings of IP Messenger?A: You can change the settings of IP Messenger by clicking on the menu icon in the main window and selecting Setup from the menu. You will see a setup window that allows you to customize various options such as appearance, behavior, network, security, log, and others. Click on the tabs to access different categories of settings. When you are done, click OK to save your changes. Q: How can I update IP Messenger to the latest version?A: You can update IP Messenger to the latest version by clicking on the menu icon in the main window and selecting Check for Updates from the menu. You will see a check for updates window that shows you the current version and the latest version of IP Messenger. If there is a new version available, click on Download Now to download it. Then, run the installer and follow the instructions to update IP Messenger. Q: How can I uninstall IP Messenger from my device?A: You can uninstall IP Messenger from your device by going to Control Panel > Programs > Uninstall. The advent of IP Messaging Service and evolution towards Converged IP Messaging. The Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) specified the SIMPLE IM technology as the first IP-based messaging 7.1Overview of the SOME/IP header This chapter describe the relevant parts of the SOME/IP header for the segmentation of SOME/IP messages. The Message Type field of the SOME/IP header contains a bit, which marks the SOME/ IP PDU as a segment of an original SOME/IP message. Every segmented SOME/IPDownload IP Messager - softsea.com
Where the DNS does not reverse match properly. 203.45.98.109 2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334 Fully Qualified Domain Name of the Source IP Type the fully-qualified remote domain name to mimic. If left null, a reverse DNS lookup will be performed on the source IP address. smtp.example.com Listener to Trace Behavior on Choose from the list of listeners configured on the system to emulate sending the test message to. InboundMail Network Owner Organization ID Type the unique identification number of the network owner, or allow the system to Lookup network owner ID associated with source IP address. You can view this information if you added network owners to sender groups via the GUI. 34 IP Reputation Score Type the IP Reputation score you want to provide for the spoofed domain, or allow the system to look up the IP Reputation score associated with the source IP address. This can be helpful when testing policies that use IP Reputation scores. Note that manually entered IP Reputation scores are not passed to the Context Adaptive Scanning Engine (CASE). See Editing IP Reputation Filtering Score Thresholds for a Listener for more information. -7.5 Envelope Sender Type the Envelope Sender of the test message. [email protected] Envelope Recipients Type a list of recipients for the test message. Separate multiple entries with commas. joe [email protected] Message Body Type the message body for the test message, including headers. Type a period on a separate line to end entering the message body. Note that “headers” are considered part of a message body (separatedIP Messaging servers in synch?
Tonyatl1 Posts: 3 Joined: Sun Sep 06, 2020 5:05 pm Mailenable does not send on correct ip I am unable to send to gmail recipients because mailenable is not using the correct ip address to send email on smtp. the message i received isReason: 550-5.7.25 [x.x.x.179] The IP address sending this message does not have a550-5.7.25 PTR record setup, or the corresponding forward DNS entry does not550-5.7.25 point to the sending IP. this statement is true. however, i have bound the smtp service to x.x.x.182 in smtp settings. why is mailenable not using the specified ip address?i thought i posted this message yesterday. i am using version 10.42 on windows server 2019. Admin Site Admin Posts: 1147 Joined: Mon Jun 10, 2002 6:31 pm Location: Melbourne, Victoria, Australia Re: Mailenable does not send on correct ip Post by Admin » Fri Nov 18, 2022 5:35 am Hi,Are you setting the outbound IP binding under the Outbound SMTP options? Check the SMTP Debug log to see if there was any problems in the sending over the specified IP address.Is Implicit messaging guarantees message delivery in Ethernet/IP
Entraîne l’expiration du délai du datagramme dès qu’il atteint le premier routeur du chemin. Ce routeur répond ensuite par un message de dépassement de délai ICMP qui indique que le datagramme a expiré. Trois autres messages UDP sont maintenant envoyés, chacun avec la valeur de TTL mise à 2, ce qui cause le deuxième routeur de renvoyer des TEM de l´ICMP. Ce processus se poursuit jusqu’à ce que les paquets atteignent l’autre destination. Comme ces datagrammes tentent d’accéder à un port non valide sur l’hôte de destination, des messages de port inaccessible ICMP sont renvoyés, indiquant que le port est inaccessible. Cet événement signale au programme Traceroute qu’il a terminé. Le but derrière ceci est d'enregistrer la source de chaque message ICMP de temps dépassé afin de fournir une trace du chemin que le paquet a pris pour atteindre la destination. Router1#traceroute 172.16.4.34 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 172.16.4.34 1 172.16.0.12 4 msec 4 msec 4 msec 2 10.0.3.23 20 msec 16 msec 16 msec 3 172.16.4.34 16 msec * 16 msec Jan 20 16:42:48.611: IP: s=172.16.12.1 (local), d=172.16.4.34 (Serial0), len 28, sendingJan 20 16:42:48.615: UDP src=39911, dst=33434Jan 20 16:42:48.635: IP: s=172.16.0.12 (Serial0), d=172.16.12.1 (Serial0), len 56, rcvd 3Jan 20 16:42:48.639: ICMP type=11, code=0 !--- ICMP Time Exceeded Message from Router2.Jan 20 16:42:48.643: IP: s=172.16.12.1 (local), d=172.16.4.34 (Serial0), len 28, sendingJan 20 16:42:48.647: UDP src=34237, dst=33435Jan 20 16:42:48.667: IP: s=172.16.0.12 (Serial0), d=172.16.12.1 (Serial0), len 56, rcvd 3Jan 20 16:42:48.671: ICMP type=11, code=0Jan 20 16:42:48.675: IP: s=172.16.12.1 (local), d=172.16.4.34 (Serial0), len 28, sendingJan 20 16:42:48.679: UDP src=33420, dst=33436Jan 20 16:42:48.699: IP: s=172.16.0.12 (Serial0), d=172.16.12.1 (Serial0), len 56, rcvd 3Jan 20 16:42:48.703: ICMP type=11, code=0 Il s’agit de la première séquence de paquets, envoyée avec une TTL = 1. Le premier routeur, dans ce cas Router2 (172.16.0.12), perd le paquet, et renvoie à la source (172.16.12.1) un message ICMP de type=11. Ceci correspond au message de temps dépassé. Jan 20 16:42:48.707: IP: s=172.16.12.1 (local), d=172.16.4.34 (Serial0), len 28, sendingJan 20 16:42:48.711: UDP src=35734, dst=33437Jan 20 16:42:48.743: IP: s=10.0.3.23 (Serial0), d=172.16.12.1 (Serial0), len 56, rcvd 3 Jan 20 16:42:48.747: ICMP type=11, code=0 !--- ICMP Time Exceeded Message from Router3.Jan 20 16:42:48.751: IP: s=172.16.12.1 (local), d=172.16.4.34 (Serial0), len 28, sendingJan 20 16:42:48.755: UDP src=36753, dst=33438Jan 20 16:42:48.787: IP: s=10.0.3.23 (Serial0), d=172.16.12.1 (Serial0), len 56, rcvd 3Jan 20 16:42:48.791: ICMP type=11, code=0Jan 20 16:42:48.795: IP: s=172.16.12.1 (local), d=172.16.4.34 (Serial0), len 28, sendingJan 20 16:42:48.799: UDP src=36561, dst=33439Jan 20 16:42:48.827: IP: s=10.0.3.23 (Serial0), d=172.16.12.1 (Serial0), len 56, rcvd 3Jan 20 16:42:48.831: ICMP type=11, code=0 Le même processus se produit pour Router3 (10.0.3.23) avec un TTL=2 : Jan 20 16:42:48.839: IP: s=172.16.12.1 (local), d=172.16.4.34 (Serial0), len 28, sendingJan 20 16:42:48.843: UDP src=34327, dst=33440JanPrivate Messaging with Twilio IP Messaging - Stack Overflow
40DHB0002UKAG Issue 2a (13/11/2001) Page 9: Busy Or Unanswered You can leave your extension number as a message for someone to call you. If their extension has a message lamp, it lights. To leave a message: 1. When NUMBER BUSY appears, press SCROLL and then press MESSAGE. 40DHB0002UKAG Issue 2a (13/11/2001) IP Office - 2030 & 2050 Phone... Page 10: Actions During A Call 1. During a call, press PROGRAM, the phone displays the software installed on your system. To do this without making a call, just press ANSWER RELEASE first. 2. Press SCROLL to return to the normal display. IP Office - 2030 & 2050 Phone 40DHB0002UKAG Issue 2a (13/11/2001) Page 11 To park all the conference parties: 1. Press PARK (see "Parking Calls (Park and Ride)" on page 15). This option is not available to the extension that created the conference. 40DHB0002UKAG Issue 2a (13/11/2001) IP Office - 2030 & 2050 Phone... Page 12: Answering Calls 1. To view any other message, press NEXT if shown. 2. To call the extension, press CALL. 3. To clear the message, press CANCEL. 4. At the last message, press AGAIN to repeat the list. IP Office - 2030 & 2050 Phone 40DHB0002UKAG Issue 2a (13/11/2001) Page 13: Answering A Call Waiting 9 indicates the number of unanswered calls that have rung your phone. Pressing the display key next to the number allows you to see the caller's number and either CALL or DELETE the entry. 40DHB0002UKAG Issue 2a (13/11/2001) IP Office - 2030 & 2050 Phone... Page 14: Transfer, Park & Hold Calls 1. Press HOLD. Do not press ANSWER RELEASE as that will end the call. 2. Retrieve the call by pressing HOLD again or make another call (enquiry call) and then press HOLD to switch between the current and held call. IP Office - 2030 & 2050 Phone 40DHB0002UKAG Issue 2a (13/11/2001) Page 15 2. Enter the phone's passcode (see "The Phone Passcode" on page 26). 3. To change the current setting, press CHANGE. 4. Press DONE and then press PROGRAM to finish. 40DHB0002UKAG Issue 2a (13/11/2001) IP Office - 2030 & 2050 Phone... Page 16: Diverting Calls ANSWER RELEASE you will hear a broken dial, but you can still make calls. Any caller will hear a ringing tone and then be connected to your voicemail. IP Office - 2030 & 2050 Phone 40DHB0002UKAG Issue 2a (13/11/2001) Page 17. The advent of IP Messaging Service and evolution towards Converged IP Messaging. The Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) specified the SIMPLE IM technology as the first IP-based messaging
GitHub - xmine64/Messager: a basic TCP/IP messager
Device and messages related to your Cloud Subscription. - Shared Device Message: The message type (Device Share) and date/time are shown at the top of the message. Page 44 • Share devices: The ‘Share devices’ option allows you to share your IP Camera with another user. Tap Share devices to open the list of devices registered to your account that are available to share. Tap on your IP Camera. The ‘Share’... Page 45 NOTE: The recipient cannot change any of your camera settings. The recipient cannot view your captured Cloud Events nor SD Card Events. Sharing IP Cameras for more information. • Sign out Tap Sign out to sign out of your IP Camera account. A message to reconfirm appears. Page 46 HELP The Help opens the Help menu. Tap Help from the Main Menu to open the ‘Help’ window. The following list of options appears: About: Tap About to open the window displaying the Smart Home Security copyright and version number. Tap Cancel to exit the ‘About’... Page 47: Navigation Bar The bottom navigation bar allows you to quickly and easily access the controls for your Smart Home Security. When selected, the navigation button appears in green. Devices: Tap Devices to open the Devices screen. The Devices screen displays the list of Vivitar Smart Home Security devices: IP Cameras, Lights, Outlets, Power Strips, Doorbell, Robobcam. Devices for more information. Page 48: Ip Cameras Screen IP CAMERAS SCREEN Tap the Devices button on the bottom navigation bar, then tap IP Cameras. One of the following screens will appear: - Live IP Camera screen: If you have only one camera connected, the Live IP Camera screen opens. - ‘IP Cameras’... Page 49 - SETTINGS: Tap to enter the selected camera’s settings. - SHARE DEVICE: Tap to enter the Share screen and follow the prompts to share your camera with another person. Note that this option is not available for a camera that is being shared. Page 50: Devices DEVICES The ‘Devices’ home screen displays the list of device types that you can control and use via the Vivitar Smart Home Security app. These devices include: IP Cameras, Lights, Outlets, Power Strips, Doorbell, and Robocam IP CAMERAS Each connected IP Camera includes the following features: •... Page 51: Sharing Ip Cameras SHARING IP CAMERAS You can share your IP Camera with another user. Your shared device can be used for viewing your IP camera’s live stream. SHARE YOUR DEVICE 1. To share your IP Camera with someone, please follow the steps below: tap the following: Menu >... Page 52 REMOVE SHARED DEVICES To remove sharing your device with another user: 1. Tap Menu > Accounts > IP Cameras > Share devices. 2.C - Sending and Receiving a TCP/IP message to an IP Address
This feature is proven to be effective especially when preventing spam and malicious emails. Web Reputation Service (WRS) and Email Reputation Service (ERS) information is used to scan email messages with URLs unknown by Trend Micro.Content Scanning can identify new spam sources in conjunction with Web Reputation Services. After enabling detect new spam sources, ScanMail performs the following actions after receiving an email message containing a URL:Web Reputation Services determines the reputation score of the URL.ScanMail uses the configured internal gateway MX record or IP address lists to determine the sender IP address of the email message.Email Reputation Services determines the reputation score of the sender IP address.Content Scanning uses the reputation scores of both the URL contained in the email message and the sender IP address to determine the risk level of the email message. Enabling Web Reputation Services allows detection of new spam sources.To enable and configure:Go to the Content Scanning screen by navigating to Spam Prevention > Content Scanning.Select Detect new spam sources to scan email messages containing URLs that may be new spam sources. You must enable Web Reputation Services to detect new spam sources.Identity your Organizational MX records or your Organizational mail gateway IP addresses: Identify your company's Organizational MX records and add the MX records to the list.Identify your company's Organizational mail gateway IP addresses and add the IP addresses to the list. Click Save.To learn more about this feature, refer to KB 1108290 (. The advent of IP Messaging Service and evolution towards Converged IP Messaging. The Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) specified the SIMPLE IM technology as the first IP-based messaging 7.1Overview of the SOME/IP header This chapter describe the relevant parts of the SOME/IP header for the segmentation of SOME/IP messages. The Message Type field of the SOME/IP header contains a bit, which marks the SOME/ IP PDU as a segment of an original SOME/IP message. Every segmented SOME/IPMODBUS MESSAGING ON TCP/IP IMPLEMENTATION
Public key encryption to exchange AES256bit symmetric keys between users. It then uses AES256bit to encrypt the message content and SHA-256 to generate the message digest. It also uses PKCS#1-v1_5 to sign or verify the messages with digital signatures.Perfect forward secrecy (PFS): IP Messenger generates a new AES256bit key for each message, and deletes it after the message is sent or received. This prevents anyone from decrypting past messages even if they obtain the RSA private key or the AES key.Message lock: IP Messenger allows you to lock your messages with a password or a fingerprint. This prevents anyone from reading your messages without your permission, even if they have access to your device or log file.Message expiration: IP Messenger lets you set an expiration time for your messages, after which they will be automatically deleted from both the sender's and the receiver's devices and log files. This reduces the risk of data leakage or unauthorized access. IP Messenger alternativesIP Messenger is not the only LAN messaging software available. There are other alternatives that you can try, depending on your needs and preferences. Here are some of them:NameDescriptionProsConsBeeBEEPA free and open-source LAN messenger that supports group chats, file sharing, voice messages, and offline messages.- Cross-platform- Easy to use- Customizable- No video calls- No encryption- No message lock or expirationLanTalk NETA paid LAN messenger that supports group chats, file sharing, voice messages, bulletin boards, and remote desktop.- Fast and reliable- Secure and encrypted- Feature-rich- Expensive- Windows-only- Complex to set upSquiggleA free and open-source LAN messenger that supports group chats, file sharing, voice calls, and emoticons.- Lightweight and portable- Peer-to-peer- Fun and colorful- No video calls- No encryption- No message lock or expirationSoftros LAN MessengerA paid LAN messenger that supports group chats, file sharing, voice calls, remote assistance, and user groups.- Secure and encrypted- Easy to install and use- Multiplatform- Expensive- No video calls- No message expirationLAN MessengerA free and open-source LAN messenger that supports group chats, file sharing, emoticons, and message history.- Cross-platform- Simple and clean- Customizable- No voice or video calls- No encryption- No message lock or expiration How to download and install IP Messenger for Windows If you want to use IP Messenger for Windows, you need to download and install it on your device. Here are the steps to do so: Download the installer from the official website The first step is to download the installer from the official website of IP Messenger. You can find it at . Choose the version that matches your Windows system (32-bit or 64-bit) and click on the download link. You will get a zip file that contains the installer and some other files. Run the installer and follow the instructions The next step is to run the installer and follow the instructions on the screen. You can extract the zip file to any location you want, or run it directly from the zip file. Double-click on the ipmsg4xx_installer.exe file to start the installation process. You will see a welcome screen thatComments
A DHCP client device acquires the IP address and the network parameters by broadcasting a UDP packet called DHCPDISCOVER within the network.Upon receiving the DHCPDISCOVER broadcast, all the non-authoritative servers discard or ignore the message. DHCP servers within the networks receive and process the broadcast packet.The DHCP Discover message contains details like: UDP Source Port 68 UDP Destination Port 67 Source IP 0.0.0.0 Destination IP 255.255.255.255 DHCPDISCOVER Packet contents Here, the source IP of the broadcast packet is 0.0.0, as the client device has not been assigned the IP address yet. With the destination IP as 255.255.255.255, the broadcast packet is sent to all the network devices, through a process called limited broadcast. Destination IP can be set to a particular subnet ID to enable a directed broadcast.Step 2: DHCP Server offers IP and network configuration parameters to client.When a valid DHCP server receives the DHCPDISCOVER broadcast message, it reserves an IP in its IP pool, and offers that IP on lease to the requesting client. It conveys its IP lease offer, the subnet mask, and default gateways to the requesting client through a DHCPOFFER message. UDP Source Port 68 UDP Destination Port 67 Source IP 192.168.31.9 Destination IP 255.255.255.255 DHCPDISCOVER Packet contents Here 192.168.31.9 is the DHCP server that offers an IP address from its pool. Traditionally, this offer message is sent to the client by specifying the clients hardware or MAC address.Step 3: Client acknowledges the required DHCP’s offer and requests the IP lease.Upon receiving a DHCPOFFER message, the client requests the assignment of the IP address offered through the DHCPOFFER message by sending a DHCPREQUEST message to the server. This message signals the DHCP server to allocate the offered IP address on lease to the client.On receiving more than one DHCPOFFER messages from the servers in the network, the client sends a DHCPREQ (DHCP Request) message only to the DHCP server whose message was received first by the client. Other offers are discarded or ignored. UDP Source Port 68 UDP Destination Port 67 Source IP 0.0.0.0 Destination IP 255.255.255.255 DHCPREQ Packet contents Step 4: DHCP Server acknowledges clients IP lease request.Upon receiving the DHCPREQUEST message, the DHCP server assigns the IP address to the client, and logs it in its data store. The server confirms the allocated IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway details by sending an DHCPACK (DHCP acknowledgement) message.The client can now start using the allocate IP and network parameters. UDP Source Port 68 UDP Destination Port 67 Source IP 192.168.31.9 Destination IP 255.255.255.255 DHCPACK Packet contents The DHCP client configures itself with the received network parameters.DHCP relay agentDevices can send broadcast messages only within the network they are a part of. They can
2025-04-18Datagram. ICMP is a separate protocol from IP, but every IP implementation must include the ICMP protocol. ICMP makes use of the IP protocol as a transport and like IP, ICMP is best-effort; an ICMP message is not guaranteed to arrive at its destination.The purpose of ICMP is to provide feedback regarding the network and datagrams, it is not to make IP a reliable transport mechanism. ICMP messages use a basic IP datagram header with the IP data being the ICMP message. The IP source address is that of the host or gateway sending the ICMP message with the destination IP address being that of the original source IP address.RFC 792 states that, where applicable, each ICMP message contains the IP header and first 64 bits of the original datagram which is used to match the datagram to a process. RFC 1812 indicates that this is no longer adequate and an ICMP message, where applicable, should contain as much of the original datagram as possible that can fit within a 576 byte message.
2025-03-31Where the DNS does not reverse match properly. 203.45.98.109 2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334 Fully Qualified Domain Name of the Source IP Type the fully-qualified remote domain name to mimic. If left null, a reverse DNS lookup will be performed on the source IP address. smtp.example.com Listener to Trace Behavior on Choose from the list of listeners configured on the system to emulate sending the test message to. InboundMail Network Owner Organization ID Type the unique identification number of the network owner, or allow the system to Lookup network owner ID associated with source IP address. You can view this information if you added network owners to sender groups via the GUI. 34 IP Reputation Score Type the IP Reputation score you want to provide for the spoofed domain, or allow the system to look up the IP Reputation score associated with the source IP address. This can be helpful when testing policies that use IP Reputation scores. Note that manually entered IP Reputation scores are not passed to the Context Adaptive Scanning Engine (CASE). See Editing IP Reputation Filtering Score Thresholds for a Listener for more information. -7.5 Envelope Sender Type the Envelope Sender of the test message. [email protected] Envelope Recipients Type a list of recipients for the test message. Separate multiple entries with commas. joe [email protected] Message Body Type the message body for the test message, including headers. Type a period on a separate line to end entering the message body. Note that “headers” are considered part of a message body (separated
2025-04-20